Dolphins, known for their friendly nature and intelligent behavior, have long captured the hearts of people around the world. Their playful antics in the wild and impressive performances in aquariums and marine parks have made them symbols of joy and companionship. However, a pressing question remains: Do dolphins attack humans? While dolphin attacks on humans are rare, they are not unheard of.
It’s essential to understand the reasons behind such behavior, the factors that can trigger it, and the potential dangers involved in human-dolphin interactions. This article delves into the nature of dolphin aggression, exploring real-life incidents, the psychology behind attacks, and how humans can interact safely with dolphins, both in the wild and in captivity.
Here’s a table summarizing the key facts and figures from the article:
| Fact/Statistic | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Dolphin Species | Over 90 species of dolphins, with bottlenose dolphins being the most widely recognized and studied. |
| Dolphin Speed | Dolphins can swim at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour. |
| Average Size of Bottlenose Dolphins | Adult bottlenose dolphins can grow up to 12 feet in length and weigh around 1,400 pounds. |
| Dolphin Intelligence | Dolphins have large brains and exhibit advanced problem-solving abilities, often demonstrating self-awareness. |
| Dolphin Communication Methods | Dolphins communicate using whistles, clicks, and body language to coordinate group activities. |
| Dolphin Attack Incidents | Notable incidents include Mihama, Japan (2022), County Clare, Ireland (2013), SeaWorld (2012), and Cancun, Mexico (2019). |
| Types of Dolphin Attacks | Attacks can include biting, ramming, and dragging, all of which can cause varying degrees of injury. |
| Mating Season Aggression | Hormonal changes during mating season can lead to aggressive behaviors, particularly among male dolphins. |
| Dolphin Pods | Dolphins live in pods that range from a few individuals to over 100 dolphins in some cases. |
| Dolphin Speed | Dolphins can travel in short bursts up to 25 mph and can stay submerged for around 10 minutes on average. |
| Number of Dolphin Species | There are approximately 90 species of dolphins across the globe, all belonging to the cetacean family. |
| Average Lifespan of Dolphins | Dolphins typically live for 20-30 years, although some individuals in the wild can exceed this range. |
Who Are Dolphins?
Overview of Dolphins
Dolphins belong to the cetacean family, which includes a diverse range of marine mammals like whales and porpoises. There are nearly 90 species of dolphins, with the bottlenose dolphin being the most recognized and commonly encountered in both the wild and in captivity. These creatures can be found in oceans around the world, from the warm coastal waters to the cooler seas further out to sea.
Dolphins are highly social and intelligent animals. They rely heavily on cooperation and communication within their pods, and their interactions with each other are vital for survival. Dolphins have large brains relative to their body size, and their intelligence is often compared to that of primates. Their communication systems, which include clicks, whistles, and body language, are some of the most sophisticated among animals. These complex behaviors allow dolphins to coordinate their movements, share information, and maintain strong social bonds.
Despite their playful nature, dolphins are also predators. They exhibit behaviors that reflect their need to hunt for food and protect themselves and their pods from threats. This dual nature of being both friendly and fierce is something to keep in mind when understanding their interactions with humans.
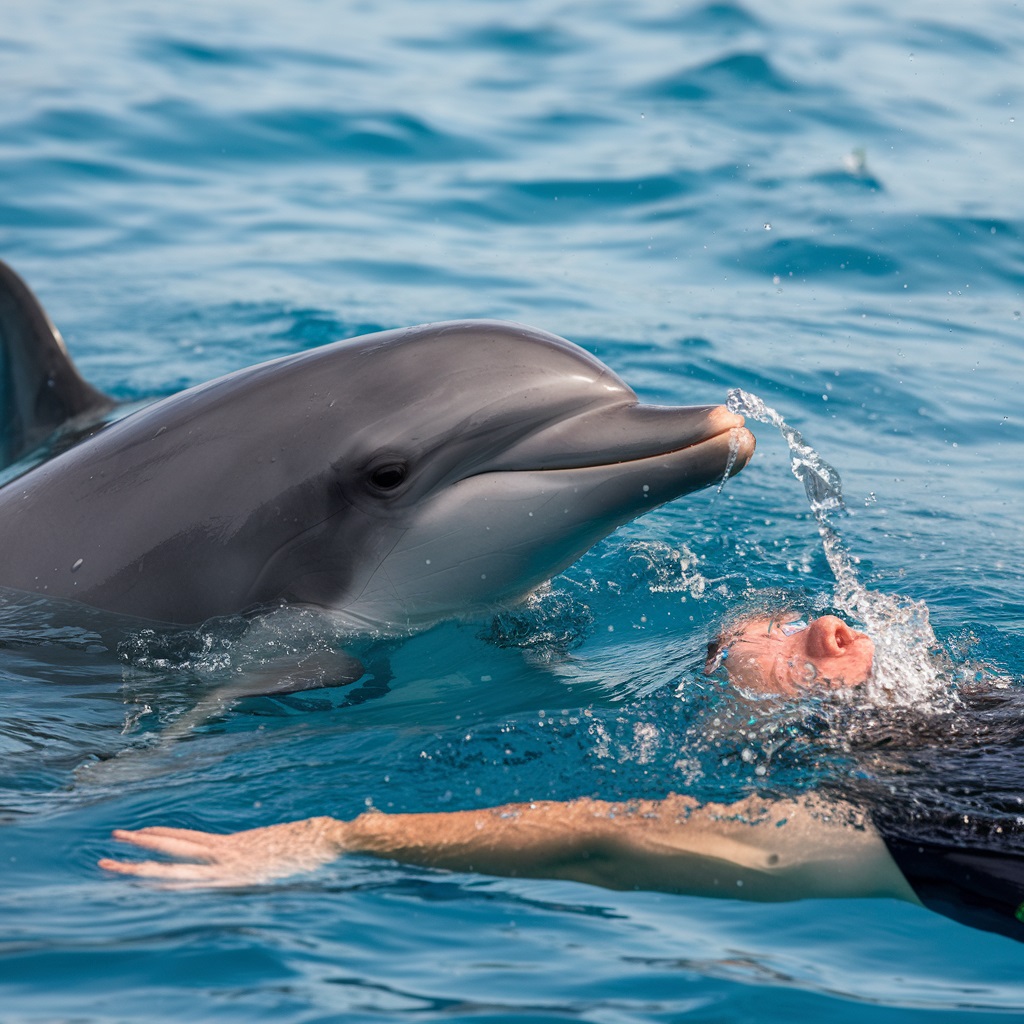

Dolphin Biology and Behavior
Dolphins are marine mammals, meaning they breathe air, are warm-blooded, and give birth to live young. They possess streamlined bodies built for swift swimming, and they can reach speeds of up to 25 miles per hour. Their large brains are a significant factor in their advanced problem-solving abilities and complex social structures.
Dolphins communicate primarily through sound. They use echolocation to navigate and hunt, producing high-pitched sounds that bounce off objects and return to the dolphin, allowing it to “see” through sound. This sensory ability is so advanced that dolphins can detect the size, shape, and movement of objects from great distances.
Interestingly, dolphins also exhibit a wide array of emotional responses, such as joy, curiosity, and playfulness. However, much like other wild animals, dolphins can become stressed, threatened, or agitated, triggering potentially dangerous behaviors.
Dolphin Social Structure
Dolphin Pods and Relationships
Dolphins are not solitary animals. They live in groups known as pods, which can vary greatly in size, from a few individuals to hundreds, depending on the species. Within these pods, dolphins form strong social bonds, and these relationships are integral to their survival.
The social structure within a pod is complex. Dolphins often form close-knit groups with clear hierarchies, with dominant individuals taking leadership roles. They communicate with each other constantly, using clicks, whistles, and body language to share information and coordinate movements, especially during hunting.
These relationships can become complicated during mating seasons when males compete for access to females. The competition can lead to aggression, both within the pod and towards outsiders. Dolphins, particularly males, may display aggressive behavior as a way to assert dominance or secure mating opportunities. These social dynamics often play a significant role in dolphin behavior, both in the wild and in captivity.
Human-Dolphin Interaction: Friend or Foe?
Historical Context and Human Interaction
For centuries, humans have had a fascination with dolphins. They are often portrayed as friendly, intelligent creatures that enjoy the company of humans. Over the years, dolphins have been featured in marine parks, like SeaWorld, and have been trained to perform tricks for audiences. In some locations, like Cancun, Mexico, tourists can even swim with dolphins in controlled environments, creating an experience that is marketed as magical and safe.
However, while these interactions are generally positive, it’s important to note that they come with inherent risks. Dolphins are wild animals with natural instincts, and while they may be trained to perform tricks, they can still exhibit aggressive behavior. Dolphin attacks on humans, though rare, have been documented in various places across the globe, underscoring the need to approach these creatures with caution and respect.
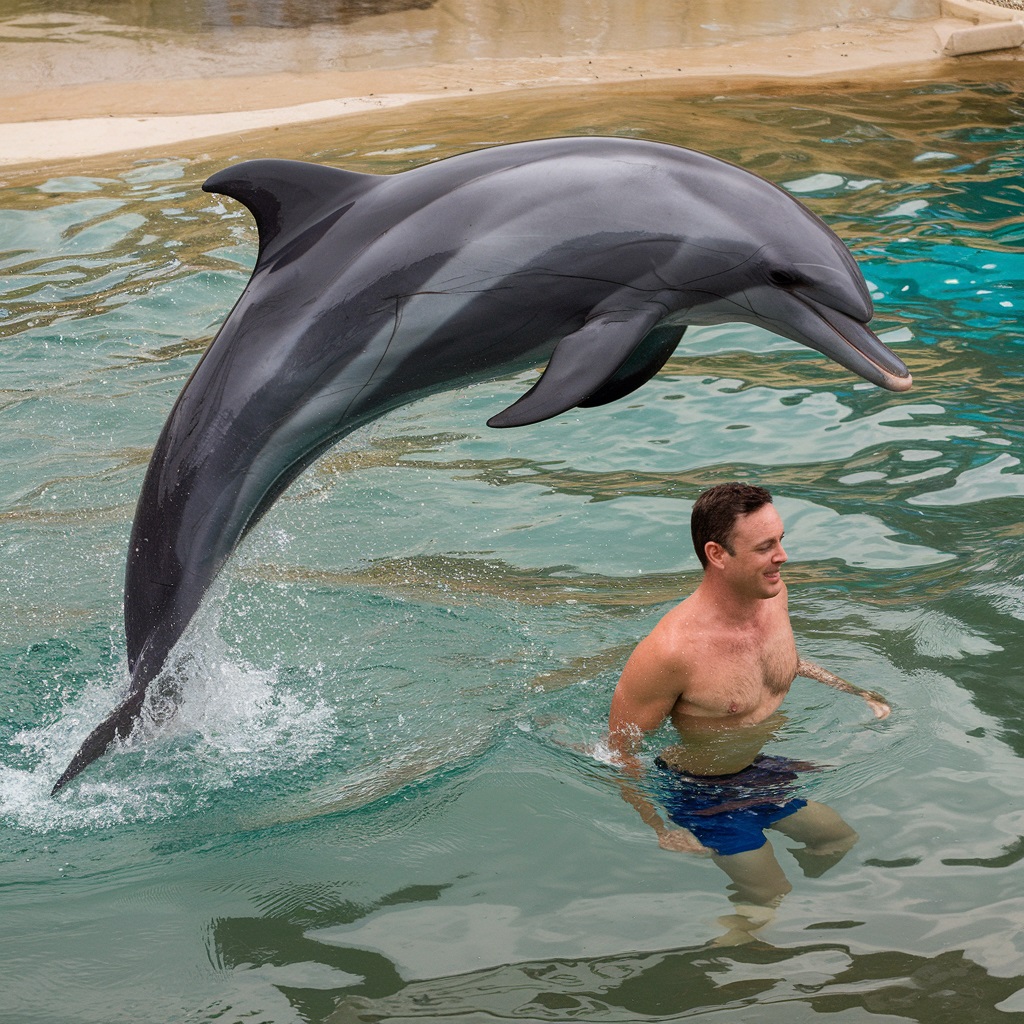

The Reality of Dolphin Attacks
While the notion of a dolphin attack on a human may seem far-fetched, incidents of aggression are more common than we realize. Dolphin aggression can occur in both the wild and in captivity, and while attacks on humans are rare, they are not isolated incidents. Some high-profile cases of dolphin aggression include:
- Mihama, Japan (2022): A dolphin in a marine park attacked multiple visitors, causing minor injuries.
- County Clare, Ireland (2013): Dusty the Dolphin, a famous attraction in the area, attacked Valerie Ryan, causing severe injuries that required hospitalization.
- SeaWorld (2012): A dolphin attacked a trainer during a show, leading to serious injury and subsequent legal action.
- Cancun, Mexico (2019): A dolphin bit a tourist during a dolphin encounter program, causing significant bruising.
These incidents highlight the fact that while dolphins are generally friendly, their behavior can turn dangerous under certain circumstances, especially when they feel threatened or stressed.
Do Dolphins Attack Humans? The Facts
Frequency of Dolphin Attacks
Dolphin attacks on humans are rare but do occur, particularly in situations where the dolphin feels threatened, stressed, or provoked. In the wild, dolphins are more likely to engage in aggressive behavior if they perceive a person as an intruder or threat to their pod. In captivity, the limited space and lack of natural stimulation can cause dolphins to become agitated and more prone to aggression.
The dolphin attack incidents mentioned earlier are outliers, but they serve as important reminders of the potential risks involved in close interactions with these animals. Experts emphasize that human interaction with dolphins should be approached with caution and respect for their space.
Types of Attacks
Dolphins may engage in a variety of aggressive behaviors if they feel provoked, threatened, or stressed. These behaviors include:
- Biting: Dolphins possess sharp teeth, and a bite can cause serious injury. Biting typically occurs if the dolphin feels threatened or is engaged in rough play.
- Ramming: Dolphins can use their powerful bodies to ram into humans, which can cause bruising or even broken bones. Ramming is often a defensive reaction or a display of dominance.
- Dragging: In some cases, dolphins have been known to grab humans and drag them underwater. This behavior is often associated with aggressive sexual behaviors or rough play and can be dangerous if the person becomes trapped underwater.
Factors That Trigger Dolphin Aggression
Several factors can contribute to dolphin aggression, including:
- Feeling Threatened: Dolphins, particularly in the wild, may attack humans if they feel their territory or pod is being invaded. The presence of humans too close to their young or their feeding grounds can trigger a defensive response.
- Stress in Captivity: Dolphins in captivity, such as those at SeaWorld, often experience significant stress due to the confinement and limited social interactions. This can lead to behavioral issues, including aggression towards humans.
- Sexual Aggression: Dolphins can exhibit sexual aggression towards humans, especially during mating seasons when their hormones fluctuate. Sexual aggression can manifest in biting, nudging, and even harassment.
- Rough Play: Dolphins are playful creatures, and their rough play can sometimes be misinterpreted as aggression. However, rough play can be dangerous, particularly in close quarters, as dolphins may not understand their strength.
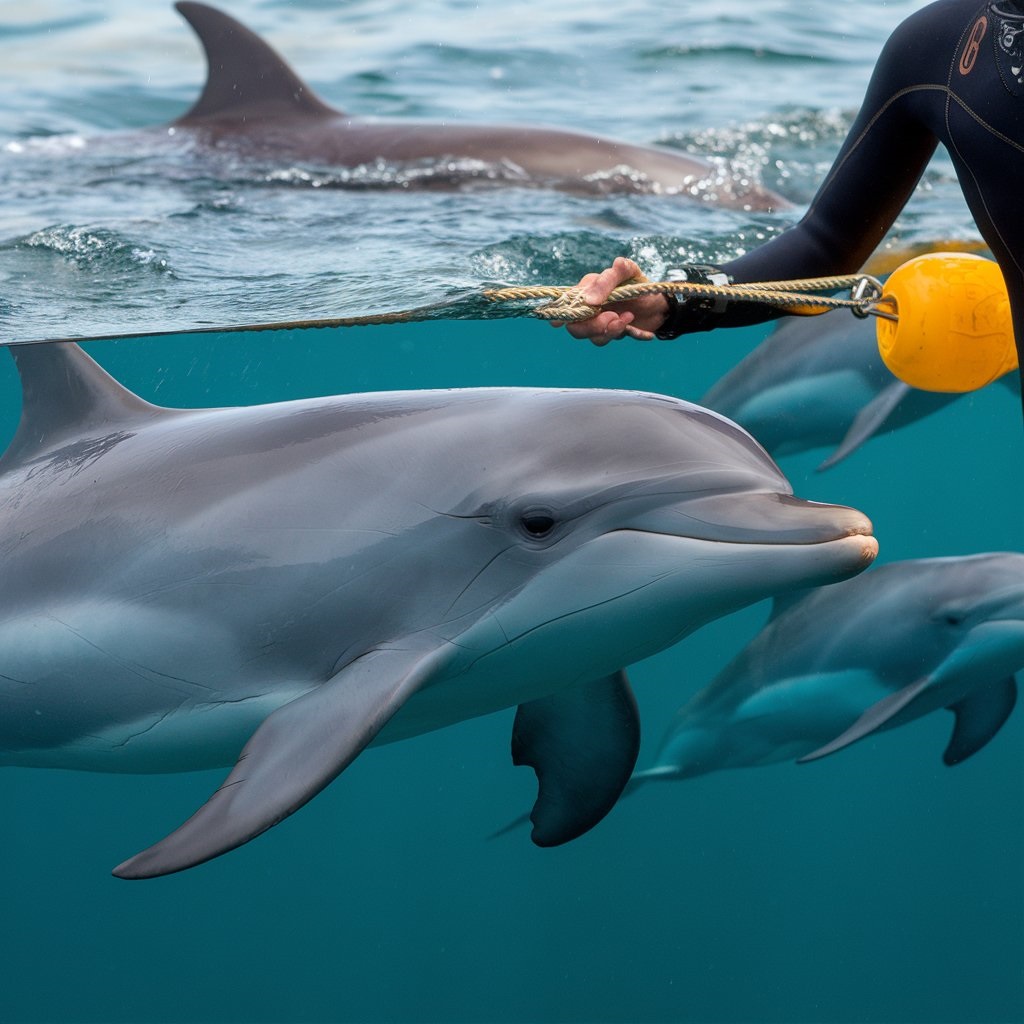
Understanding the Reasons Behind Dolphin Aggression
Stress and Hormonal Changes
Stress is a major contributing factor to dolphin aggression. Dolphins in captivity experience high levels of stress due to the unnatural living conditions they are subjected to. These conditions can cause frustration, anxiety, and even depression in dolphins, leading to increased aggression. Hormonal changes, particularly during mating seasons, can exacerbate these behaviors. Males may become more aggressive towards humans and other animals as they compete for mates.
Rough Play Turning Dangerous
While dolphins are known for their playful nature, their rough play can sometimes lead to dangerous encounters. What might seem like friendly interaction can escalate quickly if the dolphin becomes too rough or if the human is not prepared for the force behind the play.
How to Safely Interact with Dolphins
Dolphin Safety in the Wild
When encountering dolphins in the wild, it’s important to respect their space and not interfere with their natural behaviors. Follow these safety tips to ensure a safe encounter:
- Keep a safe distance: Avoid getting too close to wild dolphins. Maintaining a respectful distance helps prevent stressing or alarming them.
- Stay calm: Dolphins are sensitive to movements and sounds, so avoid splashing or making sudden, loud noises that could startle them.
- Avoid feeding them: Feeding wild dolphins can alter their natural behavior and lead to dangerous situations where they may approach humans more aggressively.
Safety in Captivity
When interacting with dolphins in captivity, always follow the safety protocols and listen to the instructions provided by the trainers. Most facilities use positive reinforcement training methods to ensure that the dolphins are calm and well-behaved, but it’s important to remain vigilant at all times.
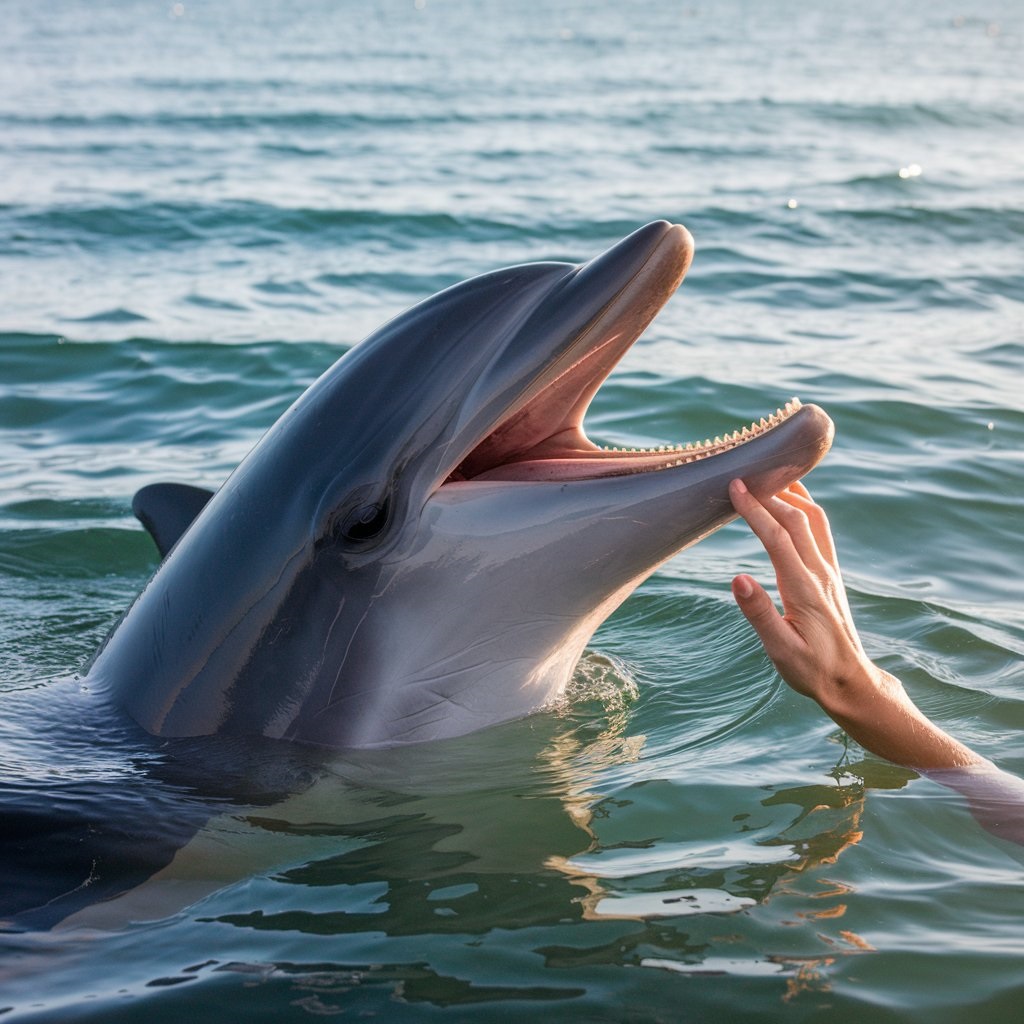

FAQs
1. Can dolphins be aggressive to humans?
Wild dolphins may become aggressive if they feel threatened, frustrated, or cornered, especially when humans try to swim with them. Dolphins that are used to human interactions may also demand food, becoming pushy if not satisfied.
2. Is it safe for humans to swim with dolphins?
Swimming with wild dolphins can be dangerous due to their unpredictable behavior and potential health risks. Dolphins may bite or carry diseases that could be transmitted to humans.
3. Will dolphins protect humans from sharks?
Dolphins have been known to protect humans from sharks, with documented cases of them circling surfers to ward off predators, as seen off the coast of New Zealand.
4. Why do sharks not attack dolphins?
Sharks are wary of dolphins due to their intelligence, detection skills, and ability to fight back in groups. Dolphins may also protect other animals, including humans, from shark attacks.
5. Can you swim with dolphins on your period?
Yes, it is safe to swim during your period, as dolphins do not have a keen sense of smell and are not attracted to blood like sharks.
6. What to do if a dolphin approaches you?
If a dolphin approaches, avoid engaging or pursuing it. It’s important to stay calm and slowly move away to avoid potential stress or aggression from the animal.
7. Why is it illegal to swim with dolphins in Hawaii?
Swimming with dolphins in Hawaii is prohibited to protect them from the disruptive effects of human interaction, which can interfere with their essential rest periods for survival.
8. Are dolphins actually friendly?
While some dolphins are curious and friendly, they are wild animals and can be unpredictable. It’s important to respect their space and not assume all dolphins are sociable.
9. Why can’t you swim with dolphins when pregnant?
Pregnant women may swim with dolphins, but activities like the Foot Push are not advisable in later stages of pregnancy due to physical limitations.
10. Why do dolphins circle humans?
Dolphins have been known to form protective circles around humans in the water, often to shield them from potential shark attacks or other threats.
11. Why are dolphins attracted to humans?
Dolphins may be drawn to humans out of curiosity or a need for companionship, especially if they are unable to find others of their species. They are also often seen following boats and snorkelers.
Conclusion: The Fine Line Between Friend and Foe
Dolphins are undoubtedly among the most intelligent and fascinating creatures on Earth. They are capable of forming deep social bonds, engaging in complex communication, and displaying behaviors that suggest empathy and playfulness. However, as with any wild animal, there is a fine line between their friendly, playful behavior and the potential for aggression.
Dolphin attacks on humans are rare but real. Understanding the reasons behind dolphin aggression and knowing how to interact with them safely can help ensure that human-dolphin encounters remain positive and enjoyable. Whether you’re observing dolphins in the wild or interacting with them in captivity, always approach them with respect, understanding, and caution. After all, while dolphins may be friendly and playful, they are still wild animals with powerful instincts.
Read more knowledgeable blogs on Flowy Magazine

James Clair is a passionate writer and researcher with a deep fascination for animal behavior and its intricate connection to human life. With a background in [relevant field of study, e.g., zoology, psychology, ethology], James has spent years studying the natural world, focusing on how animals’ actions and instincts impact human emotions, behavior, and society.
His expertise in [specific topics or regions of focus, e.g., canine psychology, animal communication, wildlife conservation] has led to numerous published works and collaborations with renowned researchers and institutions. Through his work at Flawy Magazine, James aims to bridge the gap between scientific research and public understanding, offering insightful, accessible articles that explore the complex relationship between humans and animals.
When he’s not writing, James enjoys [personal hobbies or interests, e.g., hiking in nature, volunteering at animal shelters, photography] and is an advocate for [cause or charity related to animals or conservation]. His mission is to inspire readers to see animals not just as companions or creatures of the wild, but as beings whose behavior holds valuable lessons for us all.









